What is a Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnace? Introduction to the principle of heating furnace structure
Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnaceIt is a kind of heating equipment using natural gas as fuel, which is mainly used to heat metal materials to the required forging temperature in a short time.,It has a wide range of uses, and is often used inMetal tempering,Energy conservation and environmental protection,Metal tempering,Metal melting and casting,Metal forging heating and so on,super quality and competitive price。
1、Brief introduction of Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnace
Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnaceIt is an efficient, energy-saving and environment-friendly metal heating device.,support customization。
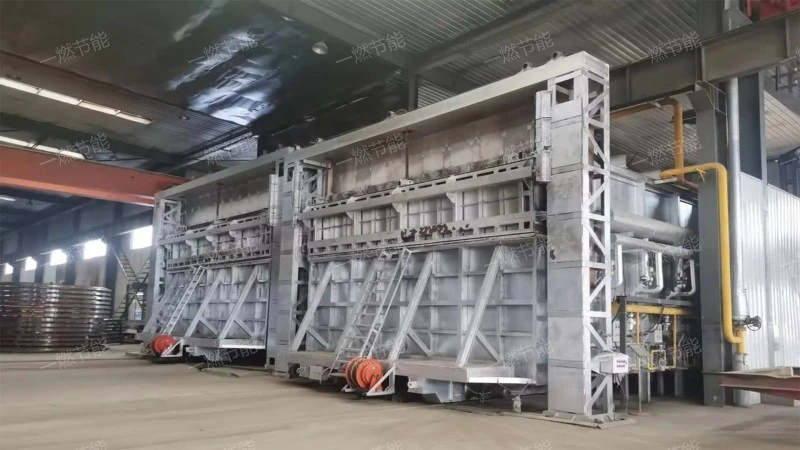

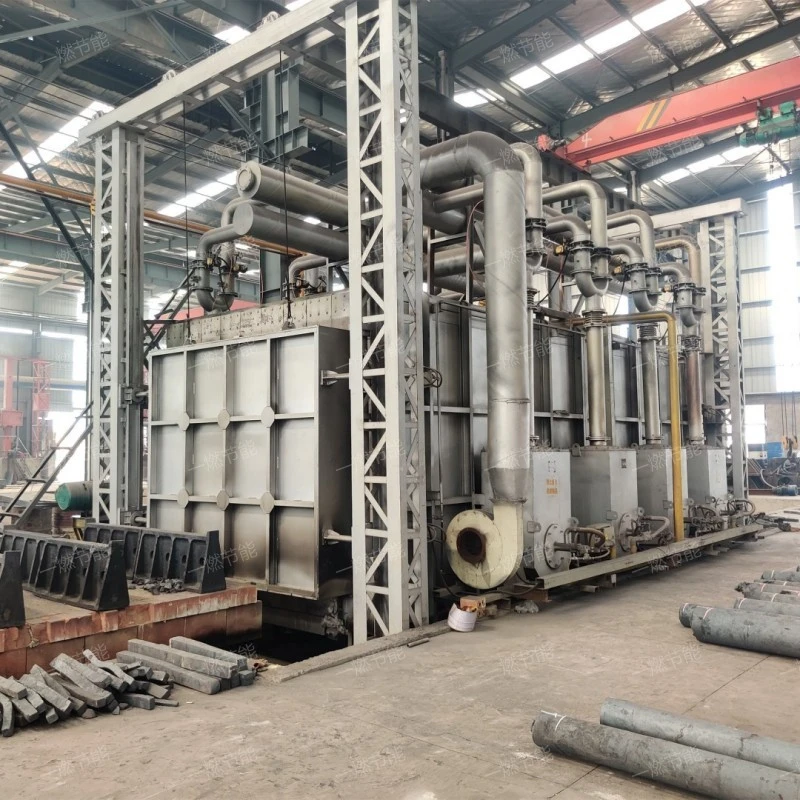
Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnace
2、Working principle of Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnace
Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnaceat runtime,The high-temperature flame and flue gas generated when fuel (natural gas) burns in the furnace are used as heat sources to heat the medium flowing in the tube to reach the specified process temperature.,the main features are Easy to control, energy-efficient, energy saving and environmental protection, Easy to maintain and Stable and reliable,widely used in surface treatment, pharmacy, machinery, material, automobile and other fields。
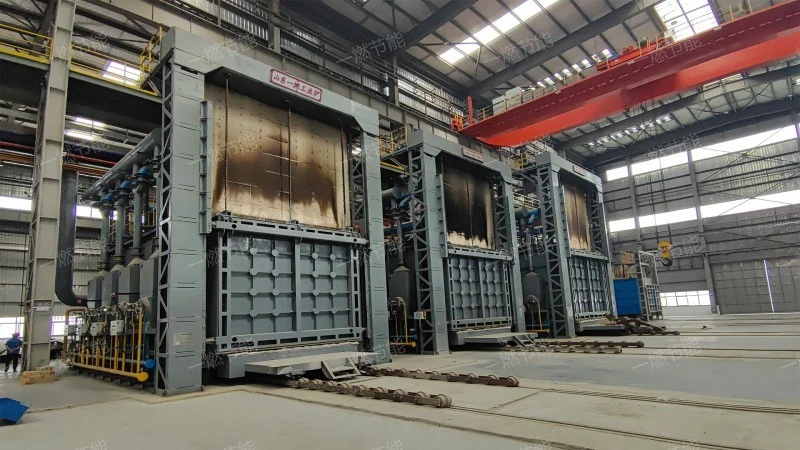

Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnace
3、Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnace application
Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnaces have the following purposes.
- Metal heat treatment
- Metal tempering
- Metal forging heating
- Improve production efficiency
- Metal melting and casting
In addition to forging heating, Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnaces can also be used for metal heat treatment processes, such as annealing and tempering. These processes can improve the microstructure and properties of metal materials, and improve their service life and mechanical properties.
By properly heating and cooling the metal material, the Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnace can realize the quenching and tempering treatment of the metal. This is helpful to adjust the hardness and toughness of metal to meet the needs of different workpieces.
The Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnace can heat the metal material to the temperature required for forging, improve its plasticity and fluidity, and thus facilitate forging. This is very important for the forging of various metal materials.
The Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnace has the advantages of fast heating speed and accurate temperature control, which can improve production efficiency. This is especially important for mass-produced forging workshops.
Although it is mainly used for forging heating, some types of Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnaces can also be used in metal melting and casting processes. This is especially suitable for melting and casting of small or special alloys.
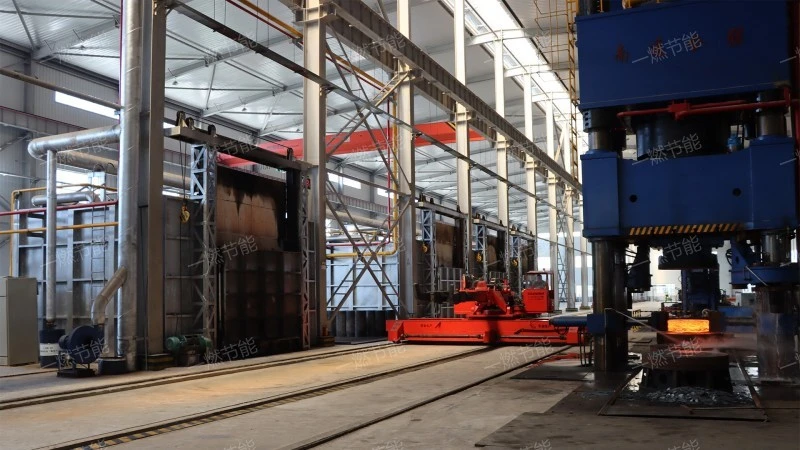

Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnace
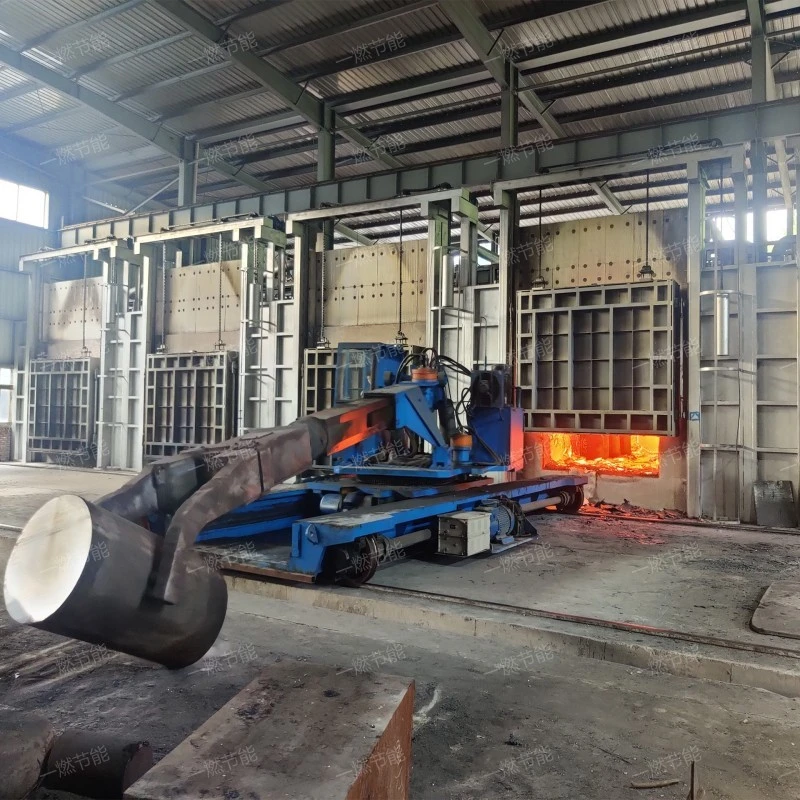
4、Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnace working site
On-site aerial photography of Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnace。
Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnace
As you can see from the live video.,One-combustion energy saving the product looks beautiful.。
5、Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnace structure composition
The Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnace has the following structure
- convection chamber
- combustor
- ventilation system
- Waste heat recovery system
- Waste heat recovery system
The material is heated by convection heat transfer of high temperature flue gas discharged from the radiation chamber. Flue gas washes the tube wall of the furnace tube at a high speed to carry out effective convection heat transfer, and its heat load accounts for about 20%-30% of the whole furnace. The convection chamber is generally arranged above the radiation chamber, and some are placed on the ground alone. In order to improve the heat transfer effect, nail head tubes or finned tubes are often used in furnace tubes.
The device that mixes natural gas with combustion-supporting air and ejects it is the core component of the heating furnace.
Ensure the gas flow in the furnace and maintain the stability of the atmosphere and temperature in the furnace.
Used to recover the exhaust heat of the heating furnace. There are two kinds of recovery methods, one is to recover by preheating combustion air, so that the recovered heat can return to the furnace again; The other is to use another recovery system to recover heat. The former is called air preheating mode, and the latter is usually called waste heat boiler mode.
Used to recover the exhaust heat of the heating furnace. There are two kinds of recovery methods, one is to recover by preheating combustion air, so that the recovered heat can return to the furnace again; The other is to use another recovery system to recover heat. The former is called air preheating mode, and the latter is usually called waste heat boiler mode.
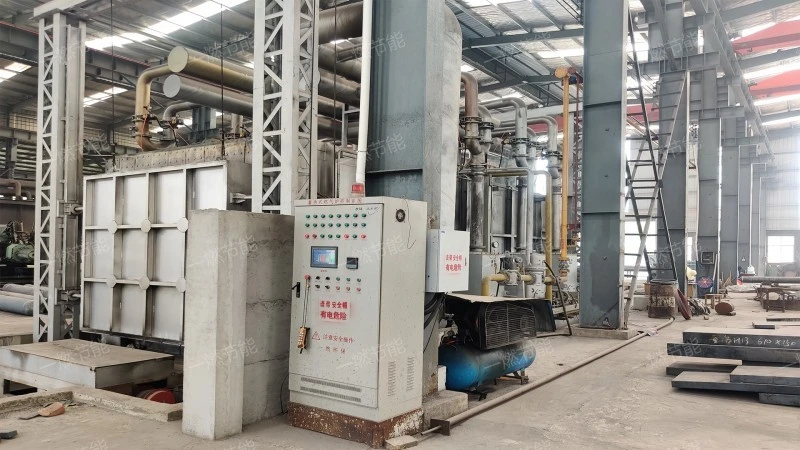

Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnace
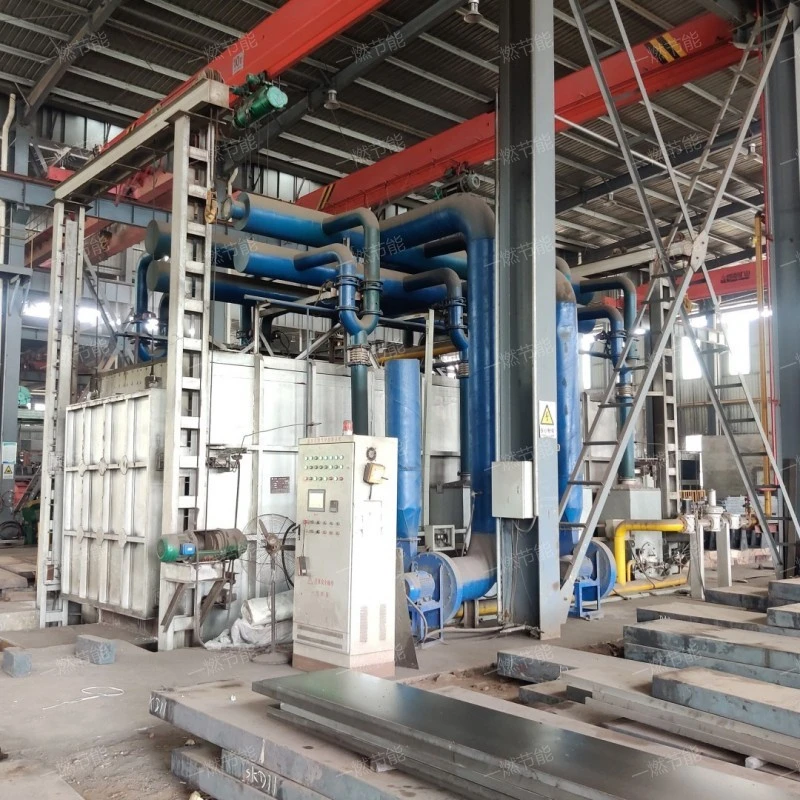
6、Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnace display
One-combustion energy saving Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnace is completely upgraded, savoring the beauty of details.。
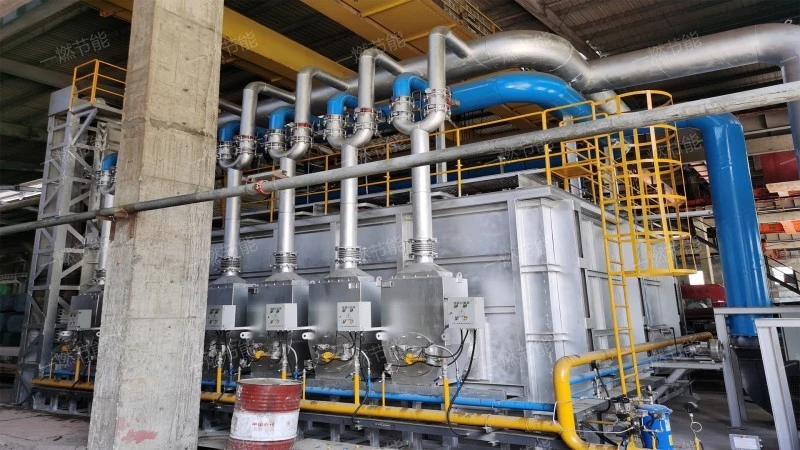

Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnace
Note: All the pictures in this article were taken by One-combustion energy saving manufacturer.。
Isothermal continuous quenching heating furnaceit has the characteristics of Strong adaptability, energy-efficient, Stable and reliable, energy saving and environmental protection and Easy to maintain,the principle is simple.Heat of combustion based on fuel. Fuel gas (such as natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas, etc.) is mixed with combustion-supporting air through the burner and burned to produce high-temperature flame and flue gas. These high-temperature flames and smoke exchange heat with metal materials in the furnace, so that they gradually heat up to the temperature required for forging.。
Related recommendation
-

What is a SCR catalytic oxidation flue gas denitrification system? Introduction to the principle of SCR denitration structure
2025-5-27 -

What is a Large trolley resistance furnace? Introduction to the advantages and characteristics of the Trolley resistance furnace
2025-5-27 -

What is a High temperature circulating trolley furnace? Introduction to the advantages and characteristics of the Forging furnace
2025-5-27 -

What is a Automatic temperature regulating trolley heating furnace? Introduction to the principle of forging furnace structure
2025-5-27 -

What is a Stepping bottom quenching and tempering furnace? Introduction to the advantages and characteristics of the forging furnace
2025-5-27 -
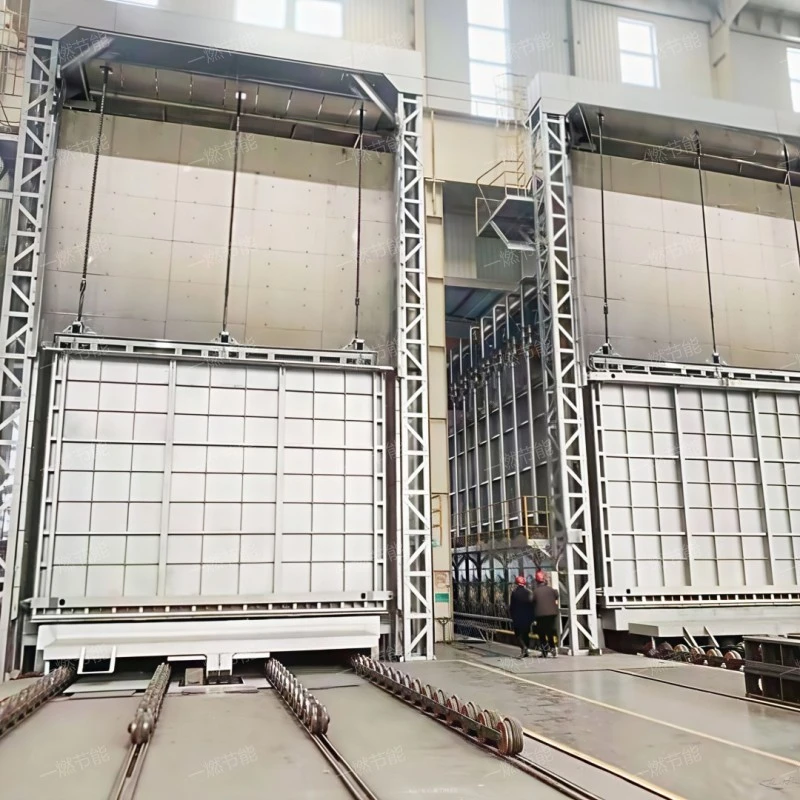
What is a Quenching and tempering treatment trolley forging furnace? Introduction to the advantages and characteristics of the forging furnace
2025-5-27 -

What is a Forging industrial heating furnace? heating furnace specifications, models, and parameters
2025-5-27 -

What is a Energy saving step heating furnace? Introduction to the Working Principle of forging furnace
2025-5-27 -

What is a Multi tube quenching furnace? Introduction to the Working Principle of heating furnace
2025-5-27 -

What is a Spheroidization annealing heat treatment furnace? heating furnace specifications, models, and parameters
2025-5-27




